You will be given a print copy of the following document to complete: http://e-conomics.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/1/7/19176587/exchange_rates_hl.pdf
0 Comments
Fixed exchange rates
Continue on with the booklet you were given to address the objectives for fixed/managed exchange rates and evaluation of the exchange rate systems (plus see textbook p290-292) Freely floating exchange rates
You will be given a copy of this to fill in... but if you lose it then here is one to download and print out... http://e-conomics.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/1/7/19176587/exchange_rates.pdf Trading blocs
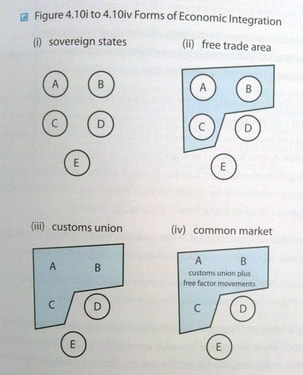
Use p314-316 of textbook plus "Economic Integration" PDF document from last session to meet the objectives listed above. Monetary union
Use p 311-312 Blink/Dorton to complete this page
Preferential trade agreements
Click here for the stages of economic integration and here for the advantages and disadvantages of trading blocs. Use the article "What is meant by Economic Integration? Is it Efficient within the EU?" to answer the following questions:
Case studies: A customs union in Africa Video: An end to the banana wars Bringing NAFTA back home
You will address these objectives in the packet you already have. Plus there are these case studies... read and answer the questions: Japan fights to protect rice farming International caviar trade banned China anger over EU shoe ruling If you have finished then look for an article on protectionism yourself... one that you might be able to use for third piece of internal assessment. Types of trade protection
As HL students you must also meet the following objectives:
You will be given a number of handouts to complete. You will need to practice drawing and explaining the graphs and also use them to make calculations.
Task 1 Use this document and page 265-266 of textbook to summarize the objectives and functions of the World Trade Organisation (WTO). Task 2 Use the internet, and in particular ‘The WTO in Brief’ section of the WTO website (www.wto.org), to do the following tasks.
Task 3 The following document contains competing views of the WTO but they are all mixed up - use annotation or highlighting to distinguish the positive views of the WTO from the criticisms made against the WTO. http://e-conomics.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/1/7/19176587/wto_advantages_disadvantages.pdf
The benefits of trade
Click here because every country is the best at something! You'll receive a packet of resources and here is some additional material: http://e-conomics.weebly.com/uploads/1/9/1/7/19176587/cartoon_macro_excerpt.pdf |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
